9. Searching Graphs¶
The search interface in GraphSpace allows a user to search for networks that have a specific attribute or tag and contain one or more nodes using simple syntax. When the user visits a matching network, GraphSpace highlights the nodes that match the search term. An identical search interface on the page for an individual network enables the user to refine the query. This interface also enables the user to search for specific edges within the network. GraphSpace allows the user to record the URL to the network with the search terms, for sharing or for further study.
9.1. Query Semantics¶
GraphSpace supports three types of search terms:
- a single string, e.g.,
wnt. In this case, GraphSpace will return a network (a) if itsnameattribute contains the query as a substring or (b) if any node in the network has aname,label, oraliasesattribute that contains the query as a substring. - two strings separated by a colon, e.g.,
name:wnt. Here, GraphSpace will return a network if thedatasection of its JSON representation contains an attribute callednamewhose value containswntas a substring. - two strings separated by two colons, e.g.,
wnt::fzd: This type of search term is only available when a user is searching a specific network. GraphSpace will highlight every edge that connects a node that matcheswntto a node that matchesfzd. This search ignores the direction of the edge.
All searches are case-insensitive. A user may specify more than one search term. When the user searches all networks, GraphSpace returns only those networks that match all the search terms. When the user is visualizing an individual network and searching within it, GraphSpace highlights nodes and edges that match any search term
9.2. Searching within Multiple Graphs¶
The user can search for search for networks that have a specific attribute or tag and contain one or more nodes using simple syntax on Graphs Page by following the given steps:
- Enter the name of the graph/node or specific network attribute mapping you are searching for in the search bar.
- Press
Enterkey or click on theSearchbutton.
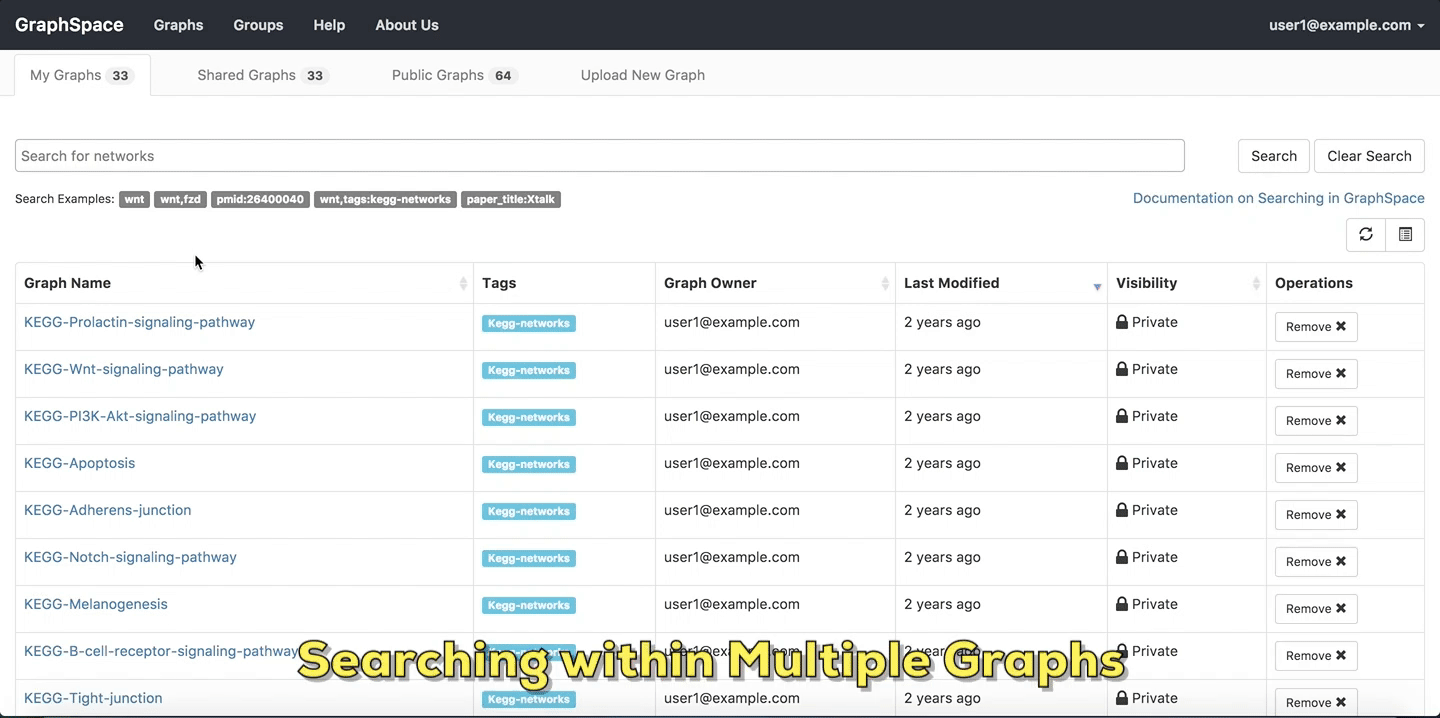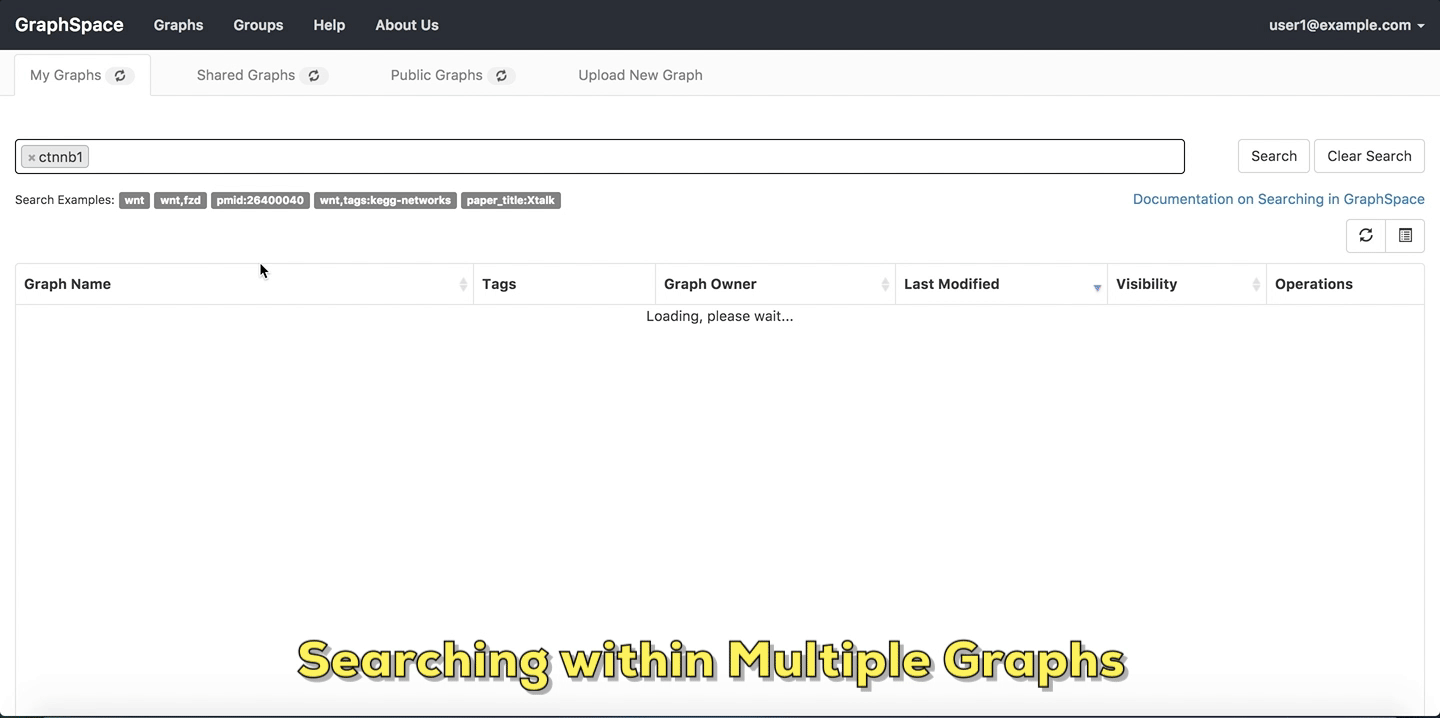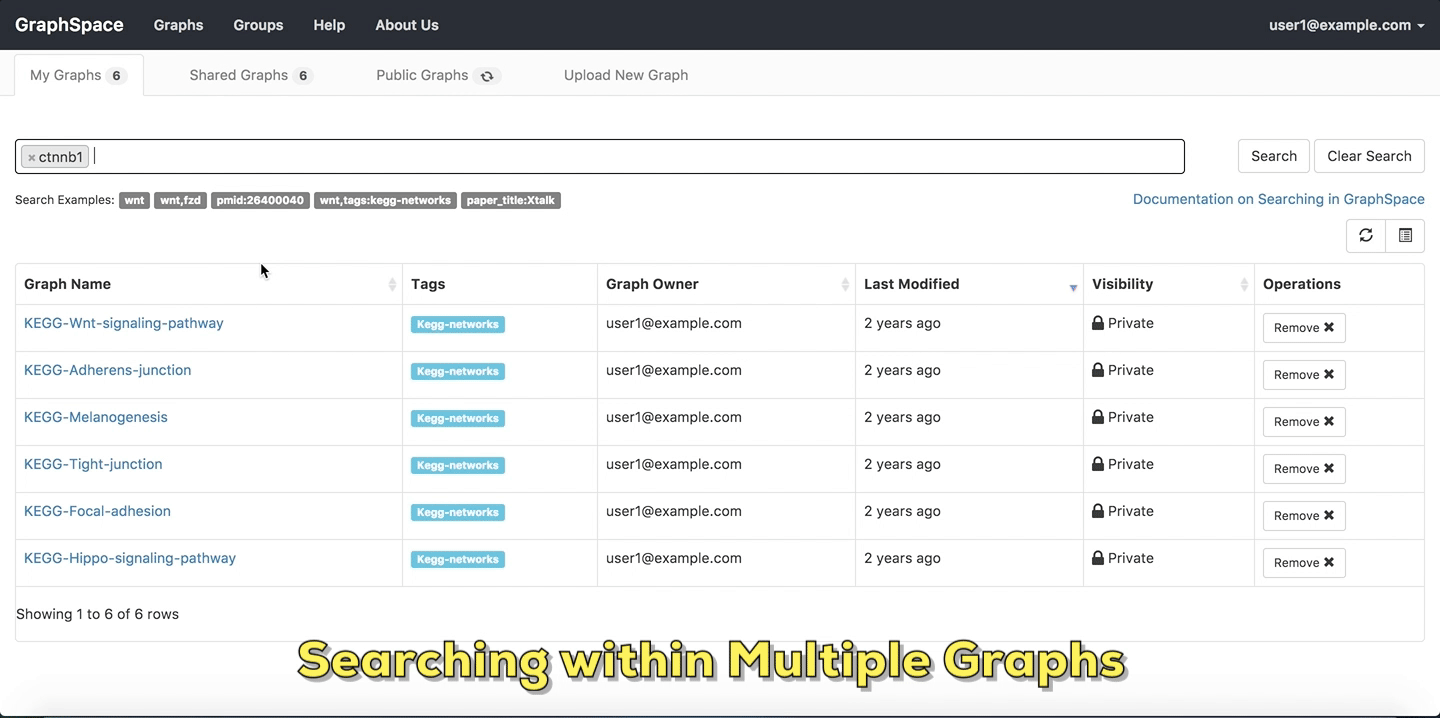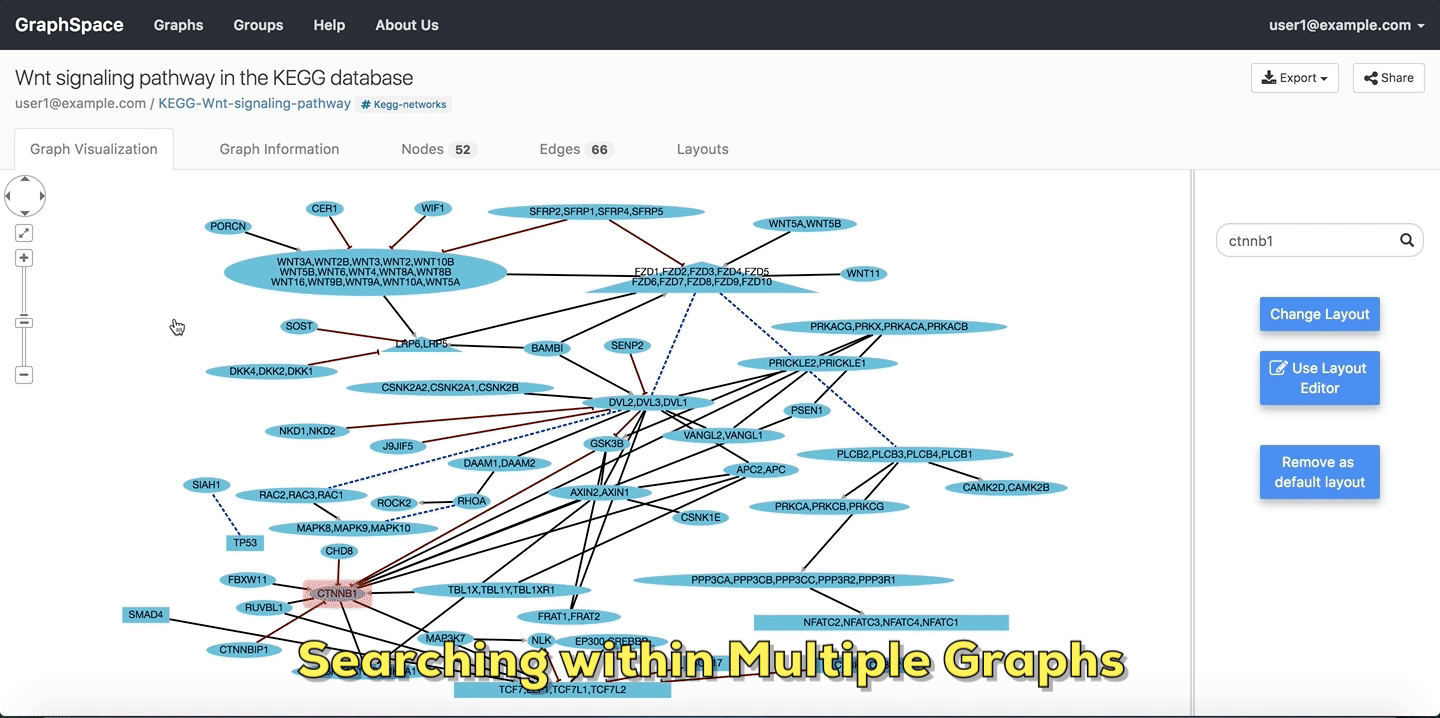
In this example, the user searches for the list for graphs that contain the protein (node) CTNNB1 (the symbol for β-catenin, a transcriptional regulator in the Wnt signaling pathway). The reduced list of graphs are the graphs where protein (node) name, label or aliases contain CTNNB1 as a substring. The match is case-insenstive. In the following example, There are six graphs owned by the user and thirty-two public graphs that contain this protein. Each link in the Graph Name column will take the user to a specific graph with the search term highlighted. In this example, the user clicks on the graph with the name KEGG-Wnt-signaling-pathway and reaches the graph for the Wnt pathway with the searched node highlighted.
 Searching within Multiple Graphs
Searching within Multiple Graphs
9.3. Searching within a Single Graph¶
The user can search for node or edges within a given graph on GraphSpace by following the given steps:
- Enter the name of the node or an edge you are searching for in the search bar.
- The nodes or edges are highlighted automatically as you type in the name of the node or edge in the search bar.
In the following example, the user searches for the graph for two proteins (nodes) CTNNB1 and WNT using the query ctnnb1, wnt. This search query highlights the proteins where protein (node) name, label or aliases contains CTNNB1 or WNT as a substring (case-insensitive). In the following example, the graph contains four nodes which match the given query.
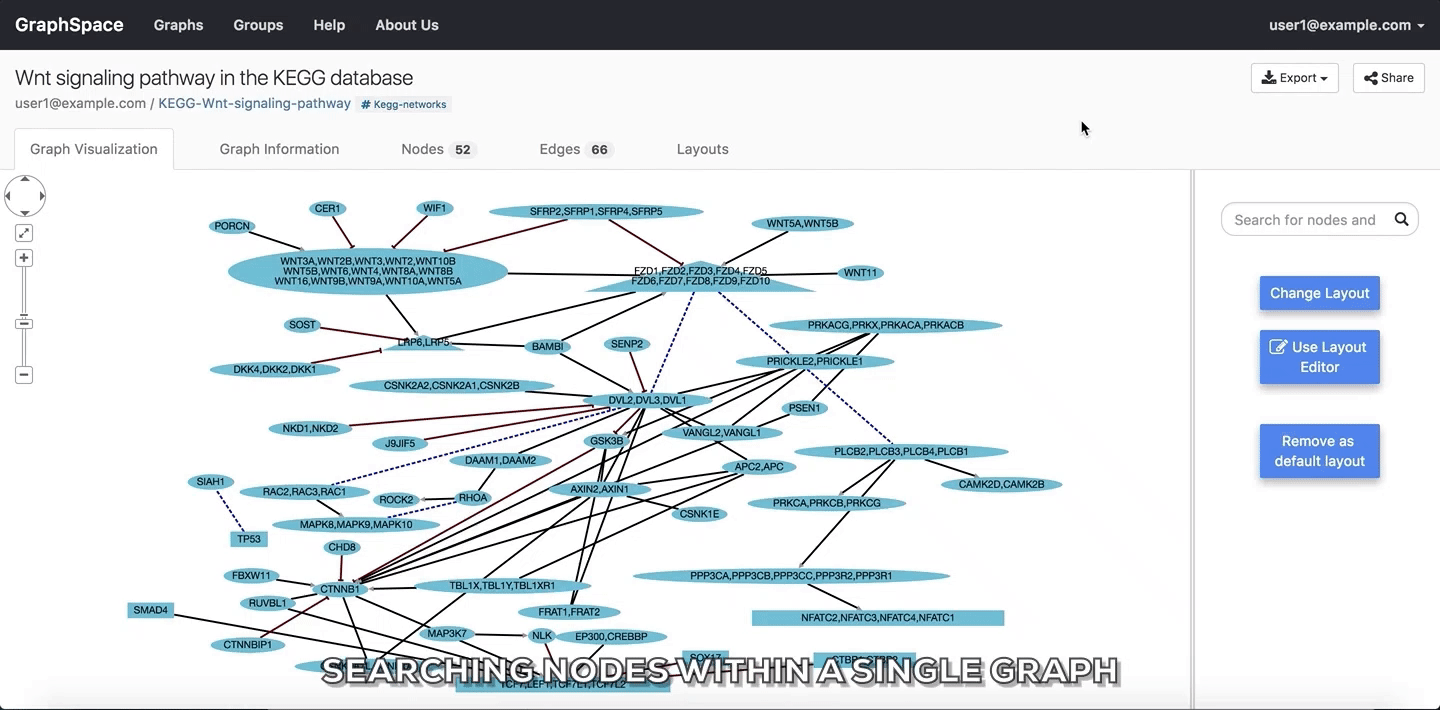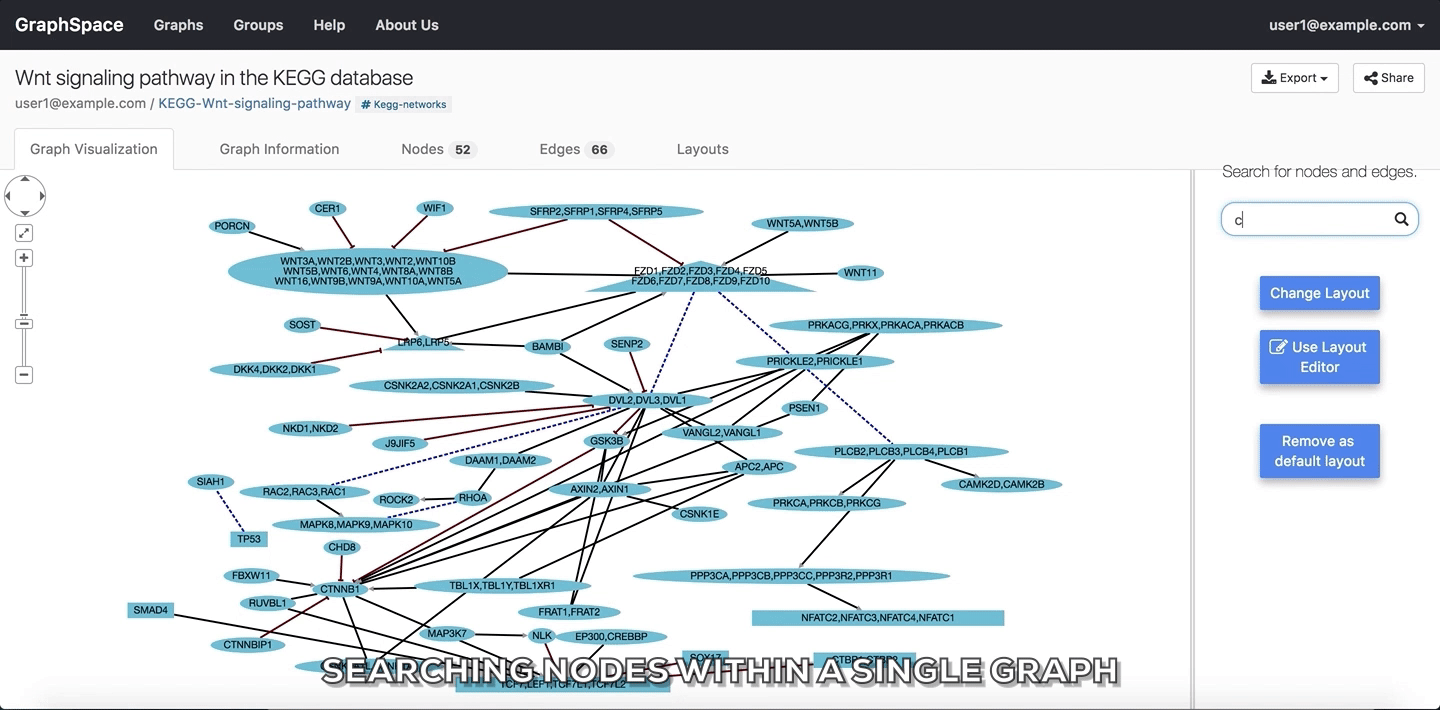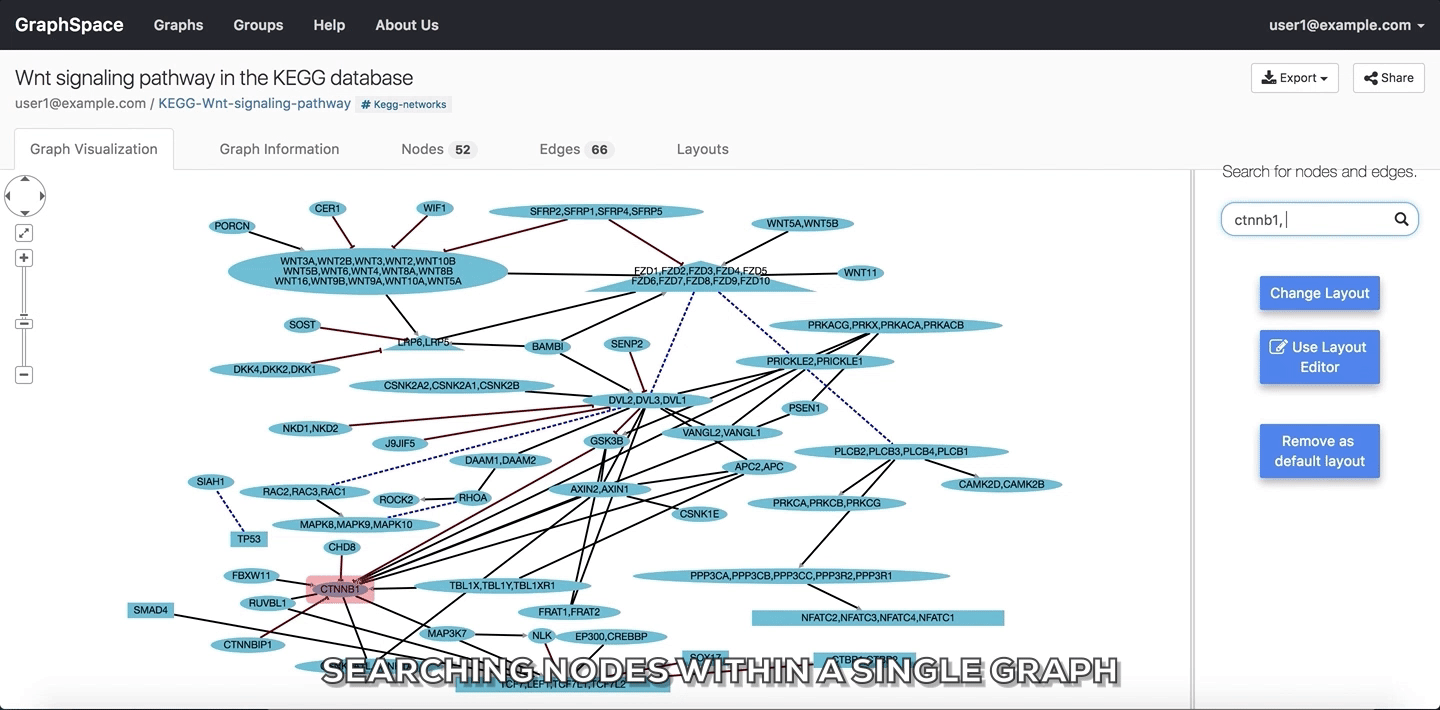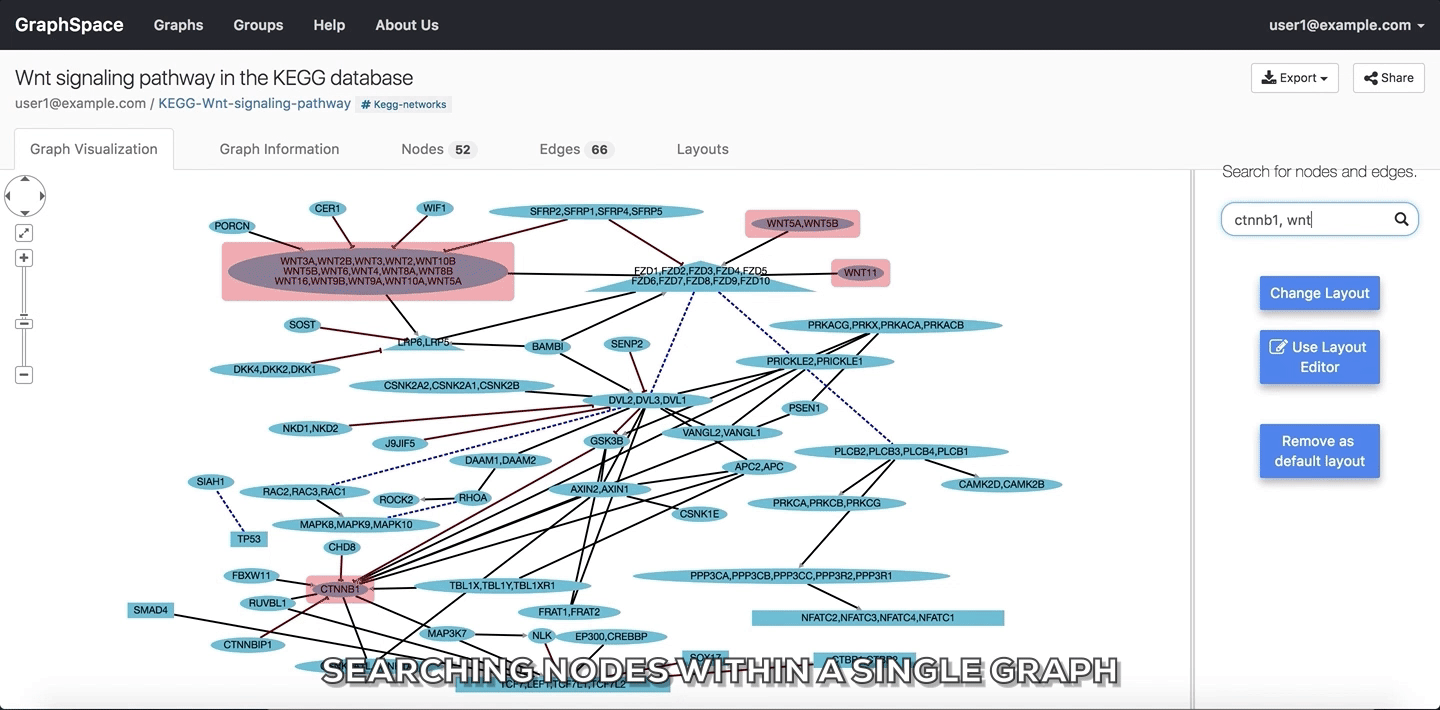 Searching nodes within a Single Graph
Searching nodes within a Single Graph
In the following example, the user searches the graph for edges from Wnt to Fzd using the query Wnt::Fzd. GraphSpace
highlights any edge whose tail node matches wnt and whose head node matches fzd. In the following example, the graph contains three edges which match the given query.
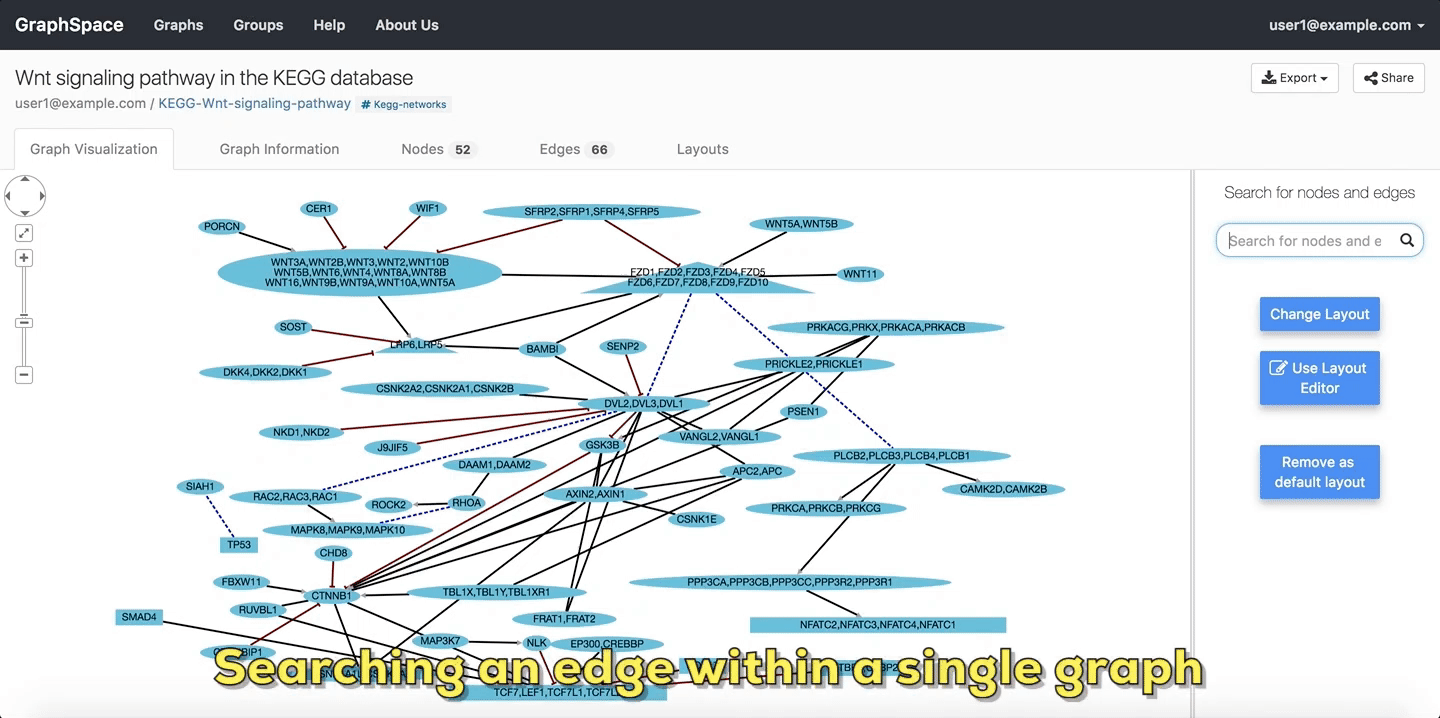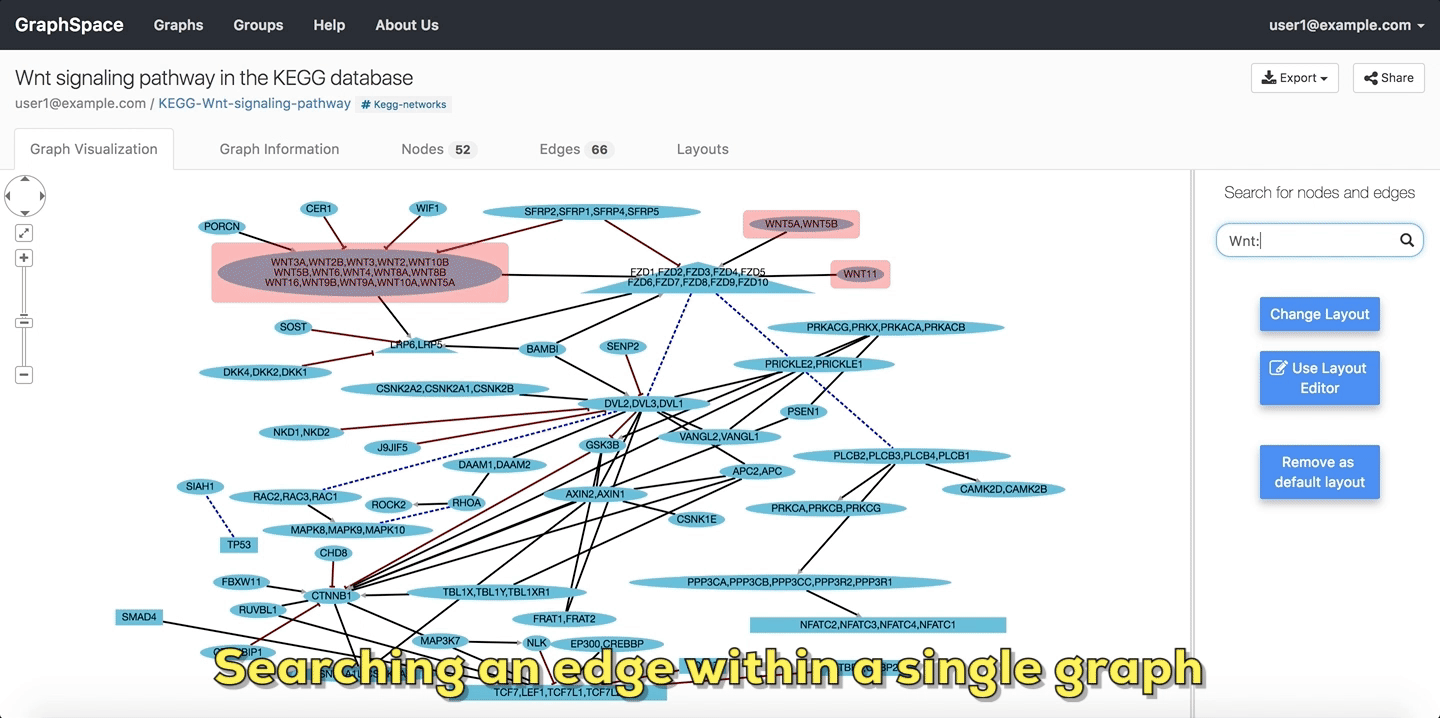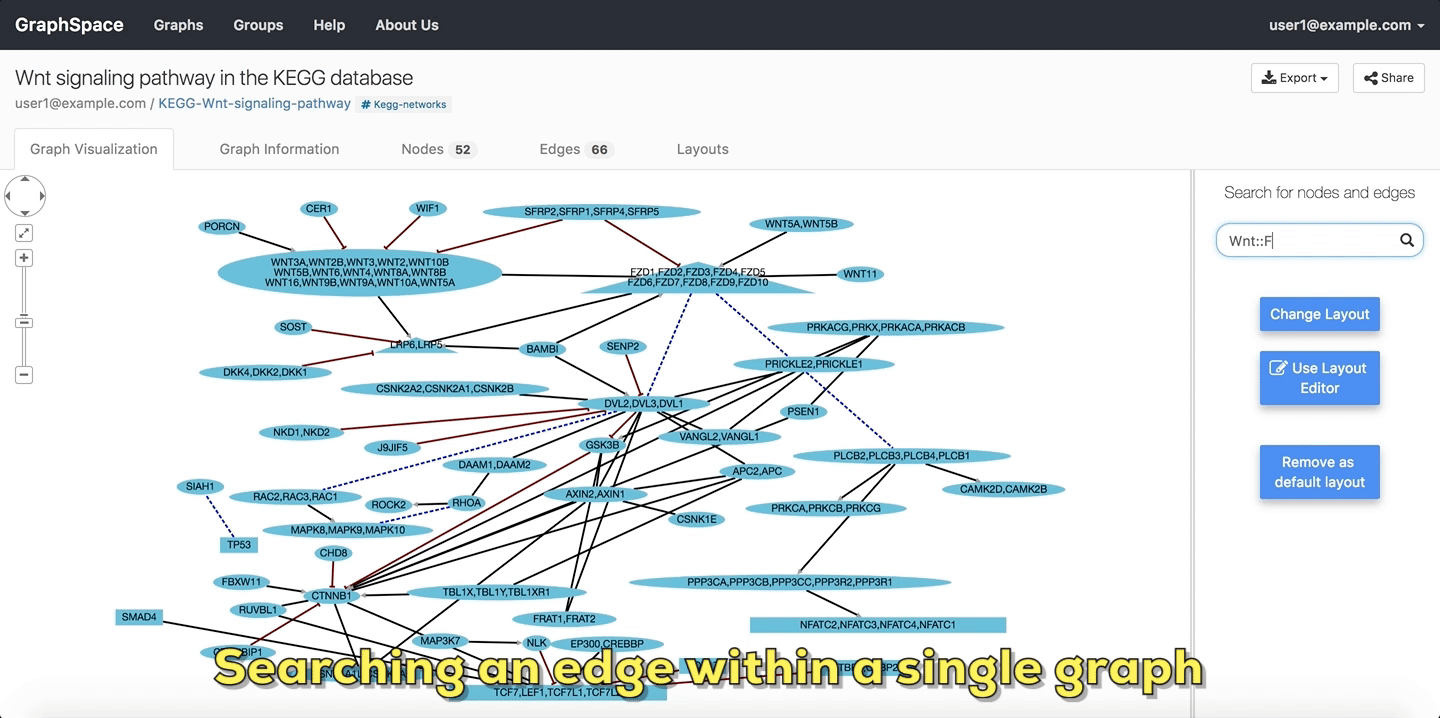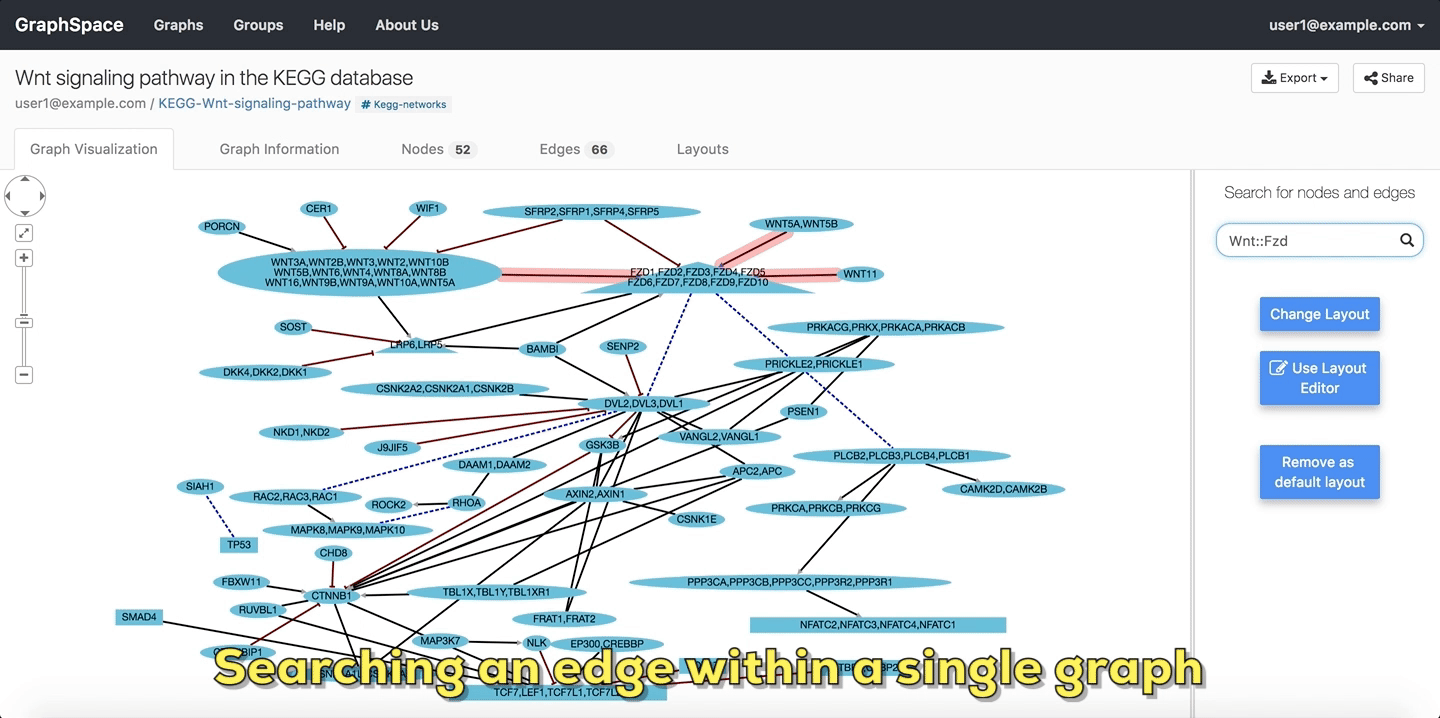 Searching edges within a Single Graph
Searching edges within a Single Graph